This blog is originally posted on Churnfree Blogs
You may have come across the word “net sales” when looking over a company’s financial documents. But what does net sales mean, and why does it matter? This article will go into detail on net sales, including what they are, how to find net sales data, and why the financial community values them so much. By the end of it, you will be able to understand the importance of net sales in finance reports, whether you are a business owner trying to make sense of your income statement or someone who is curious to learn about money-related terms in general.
Let’s understand net sales meaning.
Table of Content
Gross Sales
Returns
Allowances
Discounts
Accurate Revenue Reporting
Profitability Analysis
Sales Strategy Insights
Cash Flow
Profit Margins
Investor Confidence
Operational Decisions
What are Net Sales?
Net Sales are the total revenue received by a business after deducting sale returns, discounts, and allowances. It’s the real genuine number that shows what actually landed in the company’s pocket after adjusting for any setbacks in sales of its products or services.
Related Read: Is net sales the same as revenue?
So that was the net sales definition; let’s move towards its formula.
Net Sales Formula
Here is the net sales equation.
Net Sales = Gross sales – returns – discounts - allowances

Analysts use the net sales formula to assess how efficiently a company converts its gross sales into actual revenue. The trend of net sales over a certain time period measures if the business is growing or maintaining steady revenue or if it is facing any challenges. In short, net sales give a more accurate picture of business performance.
How to Calculate Net Sales
Here’s a quick example of how to calculate net sales: If a store sells $100,000 worth of products but has $10,000 in sales returns and $5,000 in discounts. Their net sales would be $85,000. Looks very simple, but later in the read, as you’ll see, this number carries a lot of weight when it comes to analyzing a company’s performance.
The relationship between net sales and revenue can be understood here. And here’s to understand gross sales vs net sales.
Components of Net Sales
The formula of net sales is pretty straightforward. It clearly guides what are the components that affect net sales. Let’s briefly discuss them.

Gross Sales
This is the total revenue from sales before any sort of deductions are made. Consider it the beginning point or the “ideal world” number.
Returns
These are the products that customers bring back for refunds. They are the reality of any business, whether it’s because of defective items, incorrect sizing, or just buyer’s regret. Refunds are subtracted from gross sales to get closer to true revenue.
Allowances
These are the price reductions given to customers, often as a result of minor product flaws or problems. Instead of asking for a refund, the customer may accept a small discount and keep the product. These allowances need to be subtracted from gross sales to get closer to net sales.
Discounts
These might be offered to customers as early payment incentives, promotional discounts, or bulk purchase deals. Although discounts reduce overall revenue, they increase sales significantly.
Knowing these components and obtaining their correct value is important to calculate the net sales amount.
Examples of Net Sales theory
Now that we understand the formula of net sales and its components, let’s see how net sales calculations look in real-life business.
Example of Retail Store: consider a clothing store that has a gross sale of $500,000. However, their end-of-season promotion counted up to $50,000. Their sale returns were $30,000, and $10,000 was spent as allowance for damaged clothes.
So, the net sales calculation dropped to $41,000. That is a significant difference from the original sales amount.

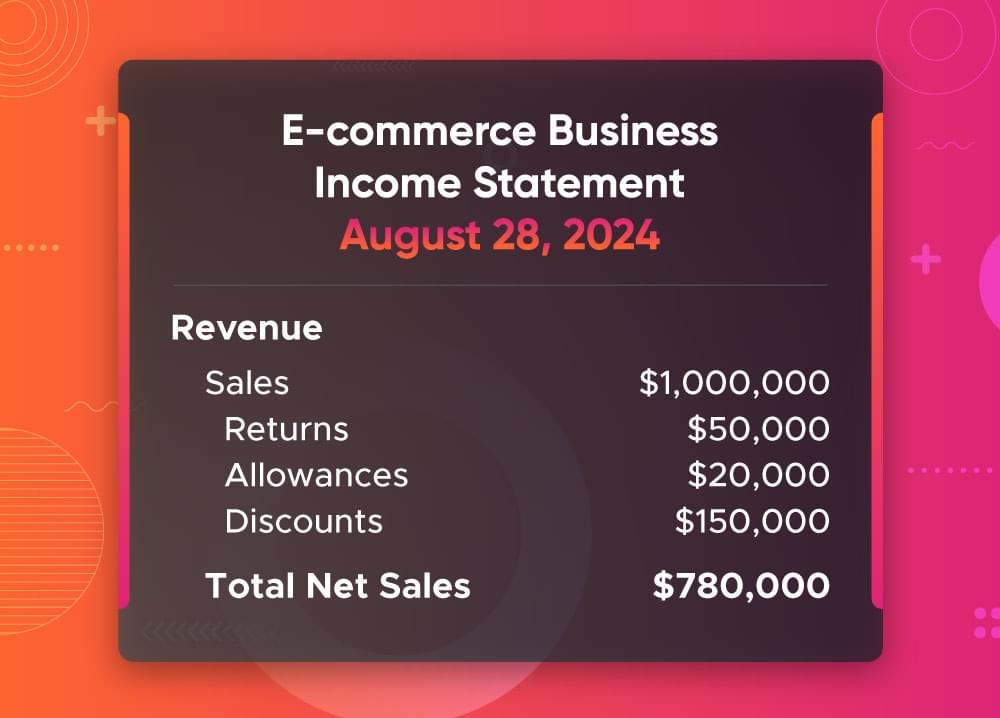
E-commerce Business Example: An online electronics retailer might have gross sales of $1 million. But if they have $150,000 in promotional discounts, $50,000 in returns, and $20,000 in allowances, their net sales end up being $780,000. This figure is what the business focuses on to gauge its profitability, not the $1 million in gross sales.
In each of these examples, net sales provide a more precise view of the business’s financial performance than gross sales would. It’s the reality check every company needs to stay on track.
Why are Net Sales Important for Income Statement
The Deloitte CFO Signals Survey (Q2 2021) includes insights from financial analysts and says that 65% of analysts view net sales as more reflective of business performance.
“Why do net sales matter so much?” you might be thinking, or “Why are net sales important for the income statement?” Well, it is one of the most important markers of a “company’s health” – its financial stability. In the Income Statement, net sales sit at the very top serving as the benchmark to determine the company’s profitability. Some companies report both these metrics.
Here’s why it’s important:

Accurate Revenue Reporting
An income statement that only displays gross sales is deceptive. It can exaggerate the income, giving board members, investors, and other relevant personnel undue confidence about business revenue. Net sales, however, provide a real picture of the revenue. It is used by investors, analysts, and business owners to help make the right decisions.
A report by Sage found that 60% of medium-sized business owners perform a comprehensive review of net sales at least once a month. This helps them with long-term planning and performance tracking.
Profitability Analysis
Net sales shall not be confused with the company’s profit. Net Sales come after deducting returns, discounts, and allowances, whereas profit comes after ALL the costs and expenses linked to running the business have been deducted from revenue. Net sales are the basis of calculations in any income statement. It affects the cost of goods sold (COGS), operational costs, and net income. If net sales are inaccurate, everything else falls apart. The McKinsey Business Finance Study (2022) outlines the profitability advantage (around 30%) for companies that consistently focus on net sales growth instead of their gross sales(PwC).
Sales Strategy Insights
Businesses can spot sales patterns and the strategies used to improve them by examining net sales. For example, if discounts are eating too much into the revenue, it might be time to rethink this sales strategy. The same is true for high returns; time to see why customers were unhappy with their purchases. PwC’s 2022 report on investor preferences shows that 80% of investors prioritize net sales when assessing revenue growth due to its clearer depiction of operational efficiency and customer satisfaction(Deloitte United States).
Gross profit is also calculated using the net sales and Cost of goods sold. Cost of goods sold (COGS) includes all the amounts associated with producing the goods or services a company sells. This would include things like materials, labor, and shipping. COGS do not count indirect expenses, such as marketing or administrative costs. And you get net sales when you remove COGS from gross sales.
To put it briefly, net sales calculation is easy and straightforward. They are used as a standard to assess the efficiency of a business’s marketing and sales strategies.
How Net Sales affect Finances
Net sales have a ripple effect on a company’s financial system. Net sales are the foundation of this system – everything above this foundation relies on how solid the foundation is. If net sales are strong, it’s easier to pay for expenses, reinvest in the company, and, of course make a profit.
Let’s look into this relationship and see how net sales affect the finances of a business.

Cash Flow
Good net sales revenue confirms a better and improved cash flow which is essential for the daily operations of the business. Businesses need a steady and smooth flow of cash to pay, for example, suppliers, employees, or any other daily obligations.
According to McKinsey, companies with higher net sales growth—20% year-over-year—report nearly double the improvement in cash flow compared to businesses with stagnant sales. This correlation comes from increased revenue enabling better operational efficiency and quicker recovery from financial downturns, leading to a stronger cash flow position overall.
Budgeting and Forecasting:
Accurate and precise net sales data help in the development of reasonable budgets and make more realistic forecasts. Businesses use this information to control product costs, growth, and future sales targets.
A study by the Association for Financial Professionals (AFP) revealed that companies with accurate sales forecasts have 10% to 15% better budget accuracy. Reliable net sales data allow organizations to plan effectively, reducing budget variances and ensuring more efficient resource allocation.
A survey by PwC found that 73% of CFOs cited declining net sales as a major factor in budget cuts and reduced capital expenditures. The decline directly impacts cash flow, limiting resources available for growth initiatives.
Profit Margins
Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Net Sales) x 100. This equation clearly shows that net sales directly affect the profit margins of any business. A higher net sales volume gives the business greater room to stand costs while maintaining profitability. On the contrary, if returns, discounts, and allowances eat up a large portion of the company’s income, then the profit margins definitely shrink.
A 10% increase in net sales can lead to a more than proportional increase in profit margins if variable costs remain stable. Companies with high net sales but poor cost management often see lower profit margins. Industries like retail often operate on lower profit margins (2-5%) due to high operating costs despite significant net sales. On the other hand, tech companies with scalable business models can achieve higher profit margins (15-25%) even if net sales fluctuate.
Investor Confidence
Investors pay close attention to net sales as a measure of a company’s performance. Consistent growth in net sales is a positive sign and can lead to increased investor confidence and a higher stock price.
According to a study by McKinsey, a 5-10% drop in net sales over consecutive quarters often results in a significant dip in investor confidence. It can lead to stock price declines as investors anticipate reduced profitability and future growth.
In tech and retail sectors, a study from PwC shows that companies that report consistent growth in net sales tend to see a 40% higher investor retention rate, compared to those with stagnating or declining sales.
Operational Decisions
Whether it’s expanding into new markets, launching new products, or cutting costs, all these decisions revolve around net sales. If a business isn’t generating enough revenue after deductions, it might need to pivot.
In a survey conducted by Deloitte, 65% of businesses reported adjusting their workforce size based on projected net sales, and a report from PwC highlighted that 40% of companies adjust their pricing strategies in response to changes in net sales.
Simply put, net sales have a domino effect on nearly every aspect of a company’s finances.
Wrapping it up
So there you have it – a summary of what are net sales, how to get net sales and why. You need to understand net sales whether you manage a business or just trying to get in financial statements.
Keeping in mind that although gross sales appear in financial statements, net sales are the true number of sales. Therefore, next time you’re looking over a financial statement, pay attention to net sales more than large-numbers to see what’s actually going on behind the scenes.
Thanks for sticking around. Here are some guides that you might want to look at:
📘Average Churn rate for subscription services
FAQs
Q: What is another name for net sales?
A: “Net revenue” or only “Sales” are other names of net sales used when preparing financial reports.
Q: Can net sales be negative?
A: Net sales can be negative if returns, allowances, and discounts exceed the gross sales. This situation indicates a significant decrease in revenue.
Q: What is net of sale?
A: “Net of sale” or “net sales” are the two names of the same term.
